Cómo solucionar eficazmente los problemas de soldadura MIG para obtener mejores resultados
MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas welding, is a popular method used in various industries for its precision and efficiency. However, like any process, it can encounter issues that can affect weld quality. Understanding how to troubleshoot MIG welding problems can significantly enhance your results and ensure your projects succeed. In this article, we will delve into important aspects of MIG weld troubleshooting, providing you with insights to help tackle common issues effectively.
Tabla de contenidos
PalancaUnderstanding Common MIG Welding Problems
Before we dive into solutions, it’s essential to recognize some of the frequent problems that may arise during MIG welding. These include issues like porosity, spatter, lack of fusion, and inconsistent penetration. Identifying the symptoms of these issues is the first step toward resolving them through proper MIG weld troubleshooting.
1. Porosity
Porosity refers to the formation of small holes in the weld, usually caused by contaminants like oil, rust, or moisture contaminating the weld area. For example, imagine working on a steel gate that has been left outdoors for a long time; it might have rust and debris that could lead to porosity if not cleaned properly before welding. One of the best MIG weld troubleshooting techniques is to ensure that the workpiece surface is clean and free from oil, dust, and other contaminants.
Here are other causes of Porosity
- Incorrect Welding Parameters: High welding speed, low heat input, or incorrect torch/gun angle can result in insufficient melting and the entrapment of gas in the weld.
- Environmental Factors: Welding in an environment with high humidity or windy conditions can affect the shielding gas coverage, leading to porosity.
- Poor Welding Technique: Such as holding the torch too far from the workpiece or inconsistent travel speed, can cause gas entrapment in the weld.

Causes and Remedies for Porosity in Welding _ Tools Focus
2. Excessive Spatter
The following factors contribute to excessive spatter in mig welding
- Improper Gas Shielding: Incorrect shielding gas type or flow rate can cause spatter. For instance, using pure CO2 as shielding gas in MIG welding tends to produce more spatter than an argon-CO2 mix.
- Contaminated Workpiece: Contaminants like rust, grease, or paint on the workpiece can cause the arc to behave erratically, leading to spatter.
- Poor Quality Material: For example Low-quality filler wires or electrodes with impurities can contribute to excessive spatter as they burn off unevenly.
- Worn or Contaminated Consumables: Using worn contact tips, nozzles, or dirty electrodes can lead to an unstable arc, resulting in more spatter.
Too much spatter during welding can lead to an uneven appearance and can even compromise the integrity of the weld. For instance, if you’re welding thin sheet metal and encounter excessive spatter, it may be due to incorrect wire feed speed or voltage settings. In this case, adjusting these settings to ensure they are appropriate for the materials being welded is a crucial troubleshooting step.

What is Weld Spatter
3. Lack of Fusion
A common MIG weld troubleshooting challenge is achieving a good fusion between the base metal and the filler material. For instance, if you’re welding a thick steel section, and you notice the bead does not fully penetrate, it can be frustrating. Lack of fusion often happens when the welder moves too quickly or uses insufficient heat. Slowing down the travel speed and ensuring adequate amperage for the material thickness can help overcome this issue.
However, it’s also essential to consider other factors that may lead to lack of fusion, such as improper joint preparation, incorrect torch angle, or using the wrong welding parameters. Addressing these elements is crucial for achieving a strong, reliable weld.
Causes of Lack of Fusion
4. Inconsistent Penetration
Inconsistent penetration can lead to weak welds that are prone to failure. For example, if you’re welding two metal plates together and observe that one section penetrates while another does not, you may need to assess your technique. Factors like torch angle, travel speed, and voltage can impact penetration. Proper MIG weld troubleshooting would involve monitoring and adjusting these variables to achieve consistent results.
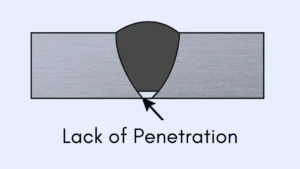
Lack of Penetration
Best Practices for Effective MIG Weld Troubleshooting
Now that you’ve identified some common issues, it’s essential to understand the best practices for troubleshooting them effectively. Here are a few strategies to consider:
1. Proper Equipment Setup
Ensure your MIG welder is set up correctly before starting. This includes selecting the appropriate wire diameter and gas type based on the materials you are welding. For instance, using 0.030-inch diameter wire with a mixed gas for mild steel can yield better results than using a smaller wire with pure CO2 gas. Proper setup is a fundamental aspect of effective MIG weld troubleshooting.
2. Maintain Clean Surfaces
As previously mentioned, clean work surfaces are vital. Use a wire brush or grinder to remove contaminants before starting your welds. Implementing a thorough cleaning routine can significantly reduce issues related to porosity and improve weld quality.
3. Monitor Voltage and Wire Feed Speed
Regularly check and calibrate your machine settings to ensure that voltage and wire feed speed are appropriate for the specific materials and thickness you are working with. For best practice, refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines, but also consider doing some test welds to find the optimal settings for your specific project.
4. Observe Welder Technique
Consider your welding technique. Factors such as travel speed, torch angle, and bead size play critical roles in weld quality. Practicing different techniques in a controlled environment can help you gain confidence and improve your skills, thus enhancing your troubleshooting ability in real projects.
5. Keep Your Equipment Maintained
Regular maintenance of your MIG welder is sometimes an overlooked aspect of troubleshooting. Inspect the gun, contact tips, and cables frequently to ensure everything is in good condition and functioning correctly. Replacing worn parts or cleaning out blockages can prevent issues before they arise.
What Customers Should Consider When Purchasing Welding Equipment
When buying a MIG welder, customers often focus on several key aspects that can affect their experience with MIG weld troubleshooting. Let’s explore these considerations:
1. Versatility
A welder that can handle various materials, such as aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel, provides greater flexibility. For instance, if you’re in a fabrication shop that deals with different metallurgies, a multi-process welder can save time and effort in switching machines.
2. Ease of Use
Look for user-friendly controls and features like automatic settings or digital displays. A welder that simplifies the setup process and provides guidance can significantly reduce the need for troubleshooting and improve efficiency.
3. Portability
For those working in multiple locations, a lightweight and portable welder is essential. This feature allows you to move around a job site without hassle while maintaining high-quality welding conditions.
4. Support and Resources
Consider manufacturers that offer excellent customer support and provide online resources. This support can be invaluable for troubleshooting issues quickly and efficiently.
Conclusión
Knowing how to effectively troubleshoot MIG welding issues is crucial for achieving better results, enhancing the quality of your work, and saving you from unnecessary frustrations. By recognizing common problems like porosity, excessive spatter, lack of fusion, and inconsistent penetration, you can target these issues with the best practices outlined above.
Remember, whether you are a professional welder or a DIY enthusiast, effective MIG weld troubleshooting is not just about fixing issues; it’s a vital skill that can lead to outstanding craftsmanship and improved project outcomes. As you continue to enhance your welding skills, always keep these strategies in mind. Addressing challenges proactively will enable you to produce high-quality welds consistently and efficiently. Make troubleshooting an integral part of your welding process, and you will reap the benefits in every project.
