Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction:
Welding is a highly sought-after skill in the metalworking industry, enabling the fabrication of strong and durable structures. One particular technique that deserves attention is square groove welding, which allows for the secure joining of metal components. In this comprehensive guide, we will take an in-depth look at how to create a square groove weld. By understanding the benefits and applications of this welding method, you can enhance your welding skills and tackle challenging projects with confidence.
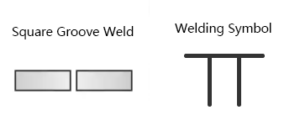
Square Groove Weld/Symbol
Source:https://www.keyence.com/ss/products/measure/welding/trouble/groove.jsp
Defining a Square Groove Weld:
A square groove weld is a type of weld joint created by filling the gap between two flat,parallel metal pieces with weld metal. This method requires less filler material, resulting in minimal deformation. However, due to its geometry, square groove welds are less suited for thick plates. Despite this limitation, they are commonly used in applications where precision and minimal material distortion are crucial, such as in the fabrication of storage tanks, pressure vessels, lightweight structures, and machinery, where smaller welding volumes are preferred.

Square Groove Weld
Source:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lEv57KVKdbs
The Process:
To create a square groove weld, follow these steps:
Step 1: Prepare the Metal
Clean and Prepare the Materials for Square Groove Welding To achieve a perfect square groove weld, it’s crucial to thoroughly clean the material surfaces. Remove any debris, rust, or oil as these impurities can lead to weld defects, weakening the final product. Use a wire brush or grinding tool for optimal cleaning results. Once clean, ensure the materials are correctly positioned with enough space for the welding electrode to easily access the groove base, which is essential for strong joint penetration.

Cleaning Before Welding
Step 2: Determine the Groove Angle
The groove angle determines the depth and shape of the joint. It is typically measured by the bevel angle, which is the angle formed by the two beveled edges. The most common groove angles for square groove welds are 45 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees. The choice of groove angle depends on the thickness and type of metal being welded.
Step 3: Cutting the Groove
To create the groove, use a cutting tool, such as a grinder or a plasma cutter, following the predetermined groove angle. Take care to make precise and clean cuts, ensuring the groove’s dimensions match the welding specifications.
Step 4: Fit-Up Alignment
Next, it’s essential to align the two metal pieces accurately. This step ensures that the final weld will have proper strength and integrity. Use clamps or fixtures to hold the workpieces in place, ensuring they are flush and aligned before proceeding.

Fit-Up Alignment
Step 5: Tack Welding
Tack welding involves making temporary welds to keep the metal pieces in place during the final welding process. This step helps maintain proper alignment and prevents any movement or distortion. Tack welds should be carefully executed, ensuring they are strong enough to hold the pieces together but easy to remove during the final weld.
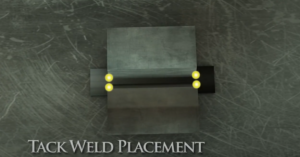
Tack Welding(Learn more about this skills)
Step 6: Welding Techniques
Now comes the crucial stage of creating the square groove weld.Several welding techniques can be used, including Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW). Among these, Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) is highly recommended for its efficiency and precision. For optimal results, consider using the MMT/PMT52W Water Cooled MIG Torch from CNAWELD. This high-performance MIG torch provides excellent heat control and arc stability, ensuring superior penetration and fusion during the welding process.
The ergonomic design of the MMT/PMT52W minimizes wrist strain, allowing welders to maintain precision over extended periods. Whether you’re working on thin sheets or heavier sections, this torch offers the reliability and durability needed for high-quality square groove welds. Explore the MMT/PMT52W Water Cooled MIG Torch today for enhanced performance in your GMAW applications.
CNAWELD KEMPPI PMT 52W
Step 7: Post-Welding Process
Once the welding is complete, remove any slag, spatter, or other welding residues using a wire brush or slag hammer. If necessary, grind the welded area to ensure a smooth, aesthetically pleasing finish. Finally, inspect the weld for any defects or discontinuities, ensuring it meets the required quality standards.
Next, inspect the weld for defects or discontinuities to ensure it meets the required quality standards. This can be done using Basic NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) Methods such as:
- Visual Testing (VT): A straightforward inspection method to identify surface-level imperfections.
- Radiographic Testing (RT) or X-ray: Used to detect internal flaws in the weld.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Effective for identifying internal discontinuities by transmitting high-frequency sound waves through the weld.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): Suitable for detecting surface and slightly subsurface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT): A simple yet effective method to identify surface-breaking defects by applying a dye or fluorescent penetrant.
By following these steps, you can ensure the weld meets structural integrity and quality requirements, providing a durable and reliable joint.
Benefits and Applications:
Square groove welds offer several benefits that make them highly desirable in various applications. Firstly, these welds provide exceptional strength and load-bearing capacity, ensuring the structural integrity of welded components. Additionally, square groove welds offer excellent fatigue resistance, making them suitable for machinery subjected to repetitive stress. Furthermore, compared to other types of welds, square groove welds require comparatively less welding material, resulting in cost savings in large-scale projects.
The applications of square groove welds are vast and varied, spanning industries such as construction, manufacturing, and transportation. In construction, these welds are commonly used in the fabrication of steel frames, beams, and columns. In the manufacturing sector, square groove welds find applications in the production of heavy machinery, equipment, and vehicles. Lastly, these welds are crucial in the fabrication of bridges and other infrastructure projects, ensuring their stability and safety.
Thought-Provoking Conclusion:
In conclusion, mastering the art of creating square groove welds is a valuable skill in the metalworking industry. By following the comprehensive guide outlined above, you can confidently undertake welding projects requiring strong and durable joints. Understanding the benefits and applications of square groove welds allows you to appreciate their significance in various industries. So, the next time you embark on a welding project, remember the power of the square groove weld and its ability to create lasting and reliable connections. Challenge yourself to further refine your welding skills and unlock new opportunities in the ever-expanding world of metal fabrication.

