Understanding Some Extremely Hazardous Materials Used in Welding Operations
Welding is a crucial process across various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive. While welding enables the creation of durable structures and parts, it also involves certain risks. Specifically, some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations include a range of fumes and gases produced during the welding process, as well as the materials involved in the welding itself. Understanding these hazards is vital for ensuring worker safety and compliance with regulations.
Key Hazardous Materials in Welding
When we discuss hazardous materials in welding, it’s important to address the distinct types of hazards present. Some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations include heavy metals, such as lead and cadmium, along with other compounds. Each of these materials poses unique risks that can severely affect health if appropriate safety measures are not adhered to.
For instance, lead is commonly present in certain welding rod coatings. When the welding takes place, and the coatings burn, they can release lead fumes into the air. Inhalation of these fumes over time can cause serious health issues, including neurological effects and respiratory problems. Companies involved in welding operations should consider using lead-free alternatives, like those utilizing titanium dioxide in their rods, to mitigate these risks. This is increasingly becoming a prevalent practice due to rising health concerns among workers and the push for safer working environments.

hazardous materials
Source: https://studiousguy.com/alloys-uses/
Fumes That Can Be Produced During Welding
In addition to hazardous materials, the welding process generates fumes that can contain various toxic compounds. Some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations include metal vapors produced from metals like zinc, chrome, and nickel. For example, welding galvanized steel releases zinc oxide fumes, leading to symptoms like “metal fume fever.” This condition can present as flu-like symptoms and can limit a worker’s ability to perform tasks during recovery.
Working in confined spaces can exacerbate the effects of fumes, making adequate ventilation essential. Using local exhaust ventilation systems can help capture fumes at the source before they disperse into the workplace air, thus protecting workers’ health.
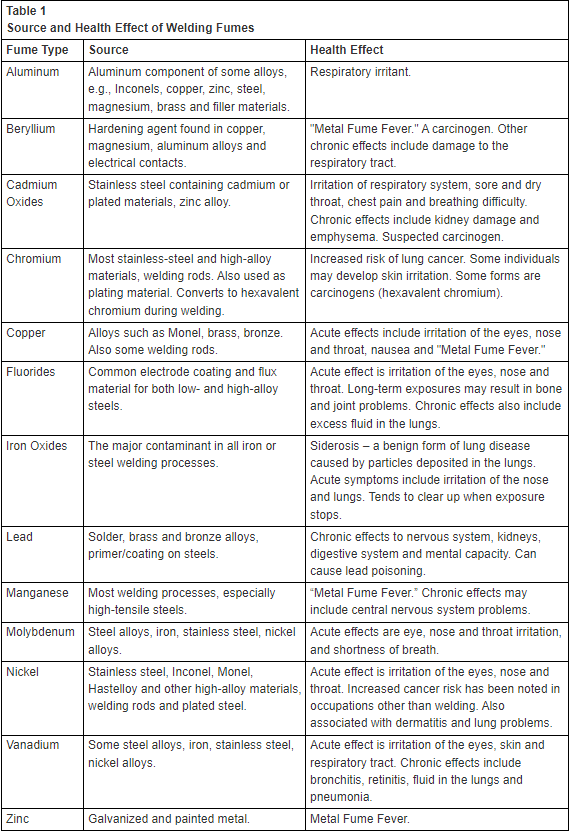
Source and Health Effect of Welding Fumes
Source:Work Safe Alberta’s Welder’s Guide to Hazards of Welding Gases and Fumes, 2009
The Role of Personal Protective Equipment
To combat the hazards of certain materials used in welding, personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a key role. Some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations necessitate the use of specific PPE, which includes protective clothing, gloves, and respiratory protective gear. For instance, when working with materials like lead or cadmium, appropriately fitted respirators are critical for preventing inhalation of toxic particles and fumes.
Moreover, protecting the eyes is equally indispensable. Welding processes generate intense light and can eject harmful particles that jeopardize eyesight. In response to this risk, CNAWELD offers its premium welding helmet, designed with advanced lens filters that not only shield against ultraviolet and infrared rays but also enhance visibility and comfort. This helmet, featuring auto-darkening technology, adapts swiftly to changes in light intensity, making it perfect for various welding environments.
Prioritizing high-quality and properly fitted PPE is essential. While occupational safety regulations set the minimum standards, investing in top-tier equipment like the CNAWELD Welding Helmet can provide significant benefits. These include improved safety, comfort, and productivity, granting peace of mind to both employers and workers engaged in high-risk welding tasks.
CNAWELD Welding Helmet
Chemical Additives and Their Hazards
Welding rods and wires may also contain chemical additives to improve properties such as weld penetration and overall weld quality. However, some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations include chemicals such as asbestos, which was historically used in some applications due to its heat resistance. Although many industries have phased out asbestos due to its known carcinogenic effects, the legacy of older equipment and structures can still pose risks today.
Furthermore, exposure to compounds like manganese is another notable concern. Manganese dust inhalation can lead to serious neurological issues resembling Parkinson’s disease, commonly referred to as “manganism.” Thus, workers involved in welding must be educated regarding avoiding materials rich in manganese or employing ventilation systems to limit exposure.
Benefits of Awareness and Training
To navigate the dangers posed by hazardous materials involved in welding, awareness and training are indispensable. Organizations can develop comprehensive safety programs focusing on the types and implications of hazardous materials. Some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations include those that can have lasting health impacts, and regular training helps keep safety front of mind.
Training should not only encompass the dangers of specific materials but also equip workers with knowledge on how to properly handle and store these materials. It can also emphasize the importance of maintaining clean work environments to limit contamination and ensure that equipment is functioning correctly.
Moving Toward Safer Practices
As industries evolve, so too does our understanding of safety. Continuous research encourages the development and adoption of new materials and processes that reduce hazards. Combined with adherence to safety protocols and education, we can mitigate the risks associated with some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations.
Emerging technologies such as automated welding systems can also contribute to reducing exposure to harmful fumes and materials. By minimizing human exposure to hazardous tasks and utilizing equipment designed with worker safety in mind, companies can enhance productivity while promoting healthier working conditions.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the hazards present in welding operations is crucial for protecting workers and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Some extremely hazardous materials used in welding operations include a variety of toxic metals, fumes, and chemical additives that can seriously impact health. By prioritizing safety training, utilizing appropriate protective equipment, and staying informed about evolving industry standards, we can create a safer working environment for everyone involved in welding.
As we advance, the importance of continually assessing the risks associated with modern materials and techniques cannot be overstated. We must remain vigilant and proactive in identifying and mitigating the dangers that arise from the materials we use, ensuring a safer future in welding operations.

