Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the Ideal Angle for the 1F T-Joint Weld?
When it comes to welding, the technique used can significantly influence the quality and strength of a joint. One such critical aspect is understanding the work angle for the 1F T-joint weld. So, how many degrees should this angle be? In this article, we will delve into the ideal angle for the 1F T-joint weld, exploring the reasons behind it and the practical applications that make this knowledge essential for anyone in the welding profession.
Understanding the 1F T-Joint Weld
Before discussing torch angles, let’s first define what the 1F T-joint weld is and its basic structure.
A T-joint is a type of weld joint where two metal pieces intersect at a right angle, forming a “T” shape. This configuration appears in applications such as automotive frames and structural assemblies.
The 1F designation means the weld is performed in the flat position, with the joint placed horizontally and the weld laid along the base metal while the upright piece remains vertical.

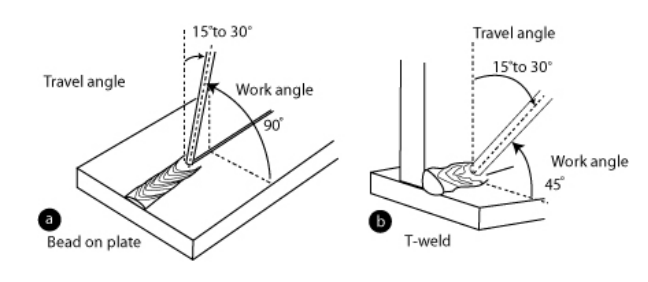
Work Angle vs Travel Angle: Setting the Right Angles for a 1F T-Joint Weld
Before setting your angles for a 1F T-joint weld, it’s important to know the difference: the work angle is the angle between the gun and the joint, viewed from above, while the travel angle is the angle in the direction of welding, viewed from the side. In most cases, you’ll use a 45° work angle to evenly split the joint and a 10–30° travel angle to maintain control of the weld pool.
Product Benefits of the Ideal Angle
The work angle for the 1F T-joint weld should be how many degrees? Understanding this angle is crucial for achieving several product benefits:
1. Stronger Welds: Utilizing an angle within the optimal range enhances the fusion between the joint materials, leading to stronger welds. This strength is vital in applications like pipeline construction, where safety cannot be compromised.
2. Reduced Defects: A precise work angle helps minimize the likelihood of defects such as porosity and undercut. This quality is crucial for industries requiring high integrity, like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
3. Efficiency: With the right angle, welders can complete tasks more quickly. A proper working angle allows for better control over the welding process, reducing the trial-and-error time spent adjusting the setup.
Factors Influencing Work Angle
While the ideal work angle for the 1F T-joint weld should be how many degrees, it’s also essential to consider external factors that might necessitate adjustments. For instance:
– Material Type: Different metals respond differently to heat. For materials that are more heat-sensitive, a shallower angle may be preferred.
– Welding Technique: The approach – whether MIG, TIG, or stick welding – can also influence the angle you’ll want to maintain during the process.
– Welder Skill Level: Experienced welders may have the competence to manage a steeper angle while maintaining control, while less experienced individuals might need to stick to the lower end of the angle spectrum.
Conclusion
In summary, the work angle for the 1F T-joint weld should be how many degrees? Ideally between 15 to 30 degrees, depending on various factors, including the materials being welded and the specific welding technique employed. Understanding this ideal angle can lead to stronger welds, fewer defects, and enhanced efficiency across various applications, from construction to shipbuilding.
By mastering the appropriate work angle, welders can significantly elevate their craft and contribute to the integrity and safety of the structures they build. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a newcomer to the trade, keeping this knowledge at your fingertips will yield tangible benefits in your welding projects. Remember, precision is key, so keep the ideal work angle for the 1F T-joint weld in mind for all your welding tasks!
